Deirdre has a hearing disability, and this article delves into the challenges faced by individuals with hearing impairments. It explores the communication barriers, social and emotional difficulties, and the impact on employment and education. Moreover, it highlights strategies for overcoming these challenges, including assistive listening devices, communication strategies, and the importance of early intervention and support services.
This article also examines the role of advocacy and awareness in promoting the rights of individuals with hearing disabilities. It discusses the work of organizations advocating for their rights, the media’s role in raising awareness, and examples of successful advocacy campaigns.
Definition of Hearing Disability
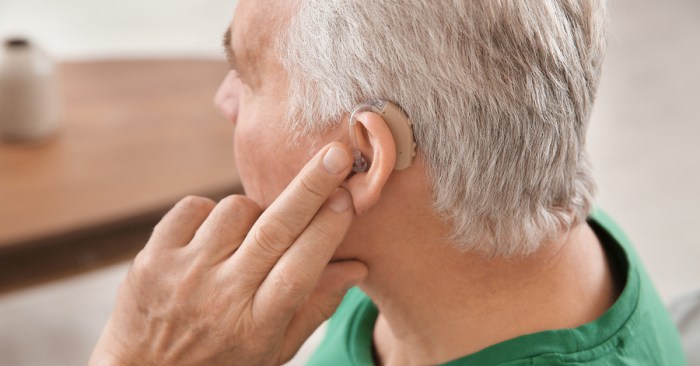
Hearing disability refers to a partial or complete inability to hear sound in one or both ears. It can range from mild to profound, affecting an individual’s ability to perceive and understand speech and environmental sounds.
Hearing disabilities can be classified into two main types: conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is unable to reach the inner ear due to blockages or damage in the outer or middle ear.
Sensorineural hearing loss, on the other hand, results from damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve, which transmits sound signals to the brain.
Examples of Hearing Disabilities
- Mild hearing loss: Individuals may have difficulty hearing faint sounds or understanding speech in noisy environments.
- Moderate hearing loss: Conversations may be challenging to follow, especially in groups or with background noise.
- Severe hearing loss: Speech may be difficult to understand even with amplification devices, and individuals may rely on lip reading or sign language.
- Profound hearing loss: Individuals may have little to no functional hearing and may rely primarily on sign language or cochlear implants.
Prevalence of Hearing Disabilities
Hearing disabilities affect a significant portion of the population worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 466 million people have disabling hearing loss, with over 34 million being children.
The prevalence of hearing loss increases with age, with older adults being more likely to experience hearing difficulties. Additionally, certain occupational hazards, genetic factors, and medical conditions can contribute to hearing loss.
Challenges Faced by Individuals with Hearing Disabilities
Individuals with hearing disabilities encounter a multitude of challenges in various aspects of life. Communication barriers, social isolation, and educational and employment obstacles are among the significant hurdles they face.
Communication Barriers
Communication poses a significant challenge for individuals with hearing disabilities. They may struggle to understand speech, especially in noisy environments. This can hinder their ability to engage in conversations, participate in meetings, or follow instructions. Additionally, they may have difficulty producing speech that is clear and intelligible to others.
Social and Emotional Challenges
Hearing disabilities can lead to social and emotional challenges. Individuals with hearing loss may experience feelings of isolation, loneliness, and frustration due to communication difficulties. They may also face stigma and discrimination from others who do not understand their condition.
These challenges can impact their self-esteem and overall well-being.
Educational and Employment Impact
Hearing disabilities can significantly impact education and employment. In educational settings, students with hearing loss may struggle to keep up with classroom discussions and lectures. They may require specialized accommodations, such as assistive listening devices or sign language interpreters, to fully participate.
In the workplace, individuals with hearing disabilities may face challenges in communication, teamwork, and safety.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges

Individuals with hearing disabilities face unique challenges in communication and daily life. Overcoming these challenges requires a combination of strategies and support systems.
Assistive Listening Devices
Assistive listening devices (ALDs) play a crucial role in enhancing communication for individuals with hearing disabilities. These devices amplify sound and transmit it directly to the listener’s ear, reducing background noise and improving speech intelligibility.
- Hearing aids:Small, electronic devices worn in the ear that amplify sound.
- Cochlear implants:Surgically implanted devices that bypass damaged parts of the inner ear, restoring hearing.
- FM systems:Wireless systems that transmit sound from a microphone directly to a receiver worn by the listener.
- Captioning:Real-time or pre-recorded text that displays spoken words on a screen.
Communication Strategies
Effective communication strategies can help individuals with hearing disabilities engage in meaningful conversations and interactions.
- Lip reading:Using visual cues from the speaker’s mouth to understand speech.
- Sign language:A visual language that uses hand gestures and facial expressions to convey meaning.
- Cued speech:A system that combines lip reading with hand cues to supplement speech.
- Written communication:Using text messages, emails, or note-taking to exchange information.
Early Intervention and Support Services
Early intervention and ongoing support services are essential for individuals with hearing disabilities to reach their full potential.
- Early detection and diagnosis:Identifying hearing loss early allows for prompt intervention and support.
- Special education programs:Schools that provide specialized instruction and support for students with hearing disabilities.
- Vocational rehabilitation:Programs that assist individuals with hearing disabilities in finding and maintaining employment.
- Community support groups:Networks of individuals with hearing disabilities and their families who provide support and information.
Advocacy and Awareness
Advocacy and awareness are crucial for improving the lives of individuals with hearing disabilities. By raising awareness, we can reduce stigma, promote understanding, and ensure that individuals with hearing disabilities have equal opportunities.
Organizations such as the National Association of the Deaf (NAD) and the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) play a vital role in advocating for the rights of individuals with hearing disabilities. They work to ensure access to education, employment, and healthcare, and they promote policies that support the well-being of this population.
Media’s Role in Raising Awareness
The media has a powerful role to play in raising awareness about hearing disabilities. By featuring stories about individuals with hearing disabilities, the media can help to break down stereotypes and promote a more inclusive society.
For example, the 2017 film “Wonder” featured a deaf character played by a deaf actor, Millicent Simmonds. The film was a critical and commercial success, and it helped to raise awareness about the challenges faced by individuals with hearing disabilities.
Successful Advocacy Campaigns
There have been a number of successful advocacy campaigns that have improved the lives of individuals with hearing disabilities.
- In 1990, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) was passed, which prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities, including those with hearing disabilities.
- In 2010, the FCC adopted new rules requiring closed captioning on all new television programming.
- In 2015, the FDA approved the first cochlear implant for children under the age of one.
These are just a few examples of the many successful advocacy campaigns that have been fought for and won by individuals with hearing disabilities and their allies.
Technology and Innovation
Advancements in technology have revolutionized communication and access to information for individuals with hearing disabilities. These technologies empower them to participate more fully in society and overcome challenges related to hearing loss.
Assistive Listening Devices
- Hearing aidsamplify sound, making it easier for individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss to hear speech and other sounds.
- Cochlear implantsare surgically implanted devices that bypass damaged parts of the inner ear and stimulate the auditory nerve, providing hearing to individuals with severe to profound hearing loss.
Communication Aids
- Closed captioningprovides written text of spoken words, making television and online videos accessible to individuals with hearing loss.
- Speech-to-text appsconvert spoken words into text, allowing individuals with hearing loss to follow conversations and participate in group discussions.
Future Technological Advancements, Deirdre has a hearing disability
Ongoing research and development promise even greater advancements in technology for individuals with hearing disabilities. These include:
- Artificial intelligence (AI)can be used to improve the accuracy and personalization of assistive listening devices.
- Brain-computer interfacescould potentially restore hearing by directly stimulating the auditory cortex of the brain.
Questions Often Asked: Deirdre Has A Hearing Disability
What is the most common type of hearing disability?
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type, caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve.
How can I communicate effectively with someone who has a hearing disability?
Use clear speech, face the person, and avoid background noise. Consider using assistive listening devices or sign language.
What are the benefits of early intervention for children with hearing disabilities?
Early intervention can improve language development, communication skills, and overall academic achievement.