For stemi patients which best describes the recommended – For STEMI patients, receiving the best recommended care is crucial for optimal outcomes. This article delves into the comprehensive management of STEMI, encompassing triage, emergency department management, invasive cardiac procedures, thrombolytic therapy, pharmacological management, lifestyle modifications, rehabilitation, and secondary prevention.
Understanding the recommended care pathways for STEMI empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions, leading to improved patient outcomes and a better quality of life.
Triage and Pre-Hospital Care
Early recognition and triage are crucial for STEMI patients to minimize delays in treatment and improve outcomes. Pre-hospital care plays a vital role in reducing time to treatment by initiating prompt assessment, administering appropriate interventions, and facilitating rapid transport to the hospital.
- Pre-hospital assessment: Rapid identification of STEMI symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and diaphoresis, is essential.
- 12-lead electrocardiography (ECG): Pre-hospital ECG can confirm the diagnosis of STEMI and guide further management.
- Oxygen therapy: Supplemental oxygen can improve tissue oxygenation and reduce myocardial ischemia.
- Aspirin: Aspirin administration can inhibit platelet aggregation and reduce the risk of thrombus formation.
- Nitrates: Nitrates can dilate coronary arteries and reduce myocardial oxygen demand.
- Morphine: Morphine can alleviate chest pain and anxiety, but should be used cautiously due to its potential for respiratory depression.
Emergency Department Management: For Stemi Patients Which Best Describes The Recommended
Upon arrival in the emergency department, STEMI patients undergo a comprehensive assessment and management protocol to stabilize their condition and initiate definitive treatment.
- Initial assessment: Includes vital sign monitoring, physical examination, and thorough history taking.
- Electrocardiography: Repeat ECGs are performed to monitor ST-segment changes and guide treatment decisions.
- Cardiac biomarkers: Cardiac biomarkers, such as troponin and creatine kinase-MB, are measured to assess myocardial damage.
- Medications:
- Aspirin and clopidogrel are administered to inhibit platelet aggregation.
- Heparin is used to prevent clot formation.
- Beta-blockers may be given to reduce heart rate and myocardial oxygen demand.
- Nitrates are used to dilate coronary arteries.
Invasive Cardiac Procedures
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is the preferred reperfusion therapy for STEMI patients with ST-segment elevation. PCI involves inserting a catheter into the coronary artery and using a balloon or stent to open the blocked vessel.
- Indications:
- Persistent ST-segment elevation despite medical therapy.
- Hemodynamic instability.
- Cardiogenic shock.
- Contraindications:
- Severe bleeding disorders.
- Active endocarditis.
- Uncontrolled hypertension.
- Types of PCI techniques:
- Balloon angioplasty: Uses a balloon to widen the narrowed artery.
- Stent placement: Uses a metal scaffold to keep the artery open.
- Atherectomy: Removes plaque from the artery.
Thrombolytic Therapy
Thrombolytic therapy involves administering clot-busting medications to dissolve thrombi in the coronary arteries. This therapy is less commonly used than PCI but may be considered in patients who are not candidates for PCI.
- Types of thrombolytic agents:
- Streptokinase
- Alteplase
- Tenecteplase
- Mechanisms of action: Thrombolytic agents convert plasminogen to plasmin, which dissolves fibrin clots.
- Benefits: Rapid thrombolysis and reperfusion of the coronary artery.
- Risks: Bleeding, intracranial hemorrhage, and allergic reactions.
Pharmacological Management
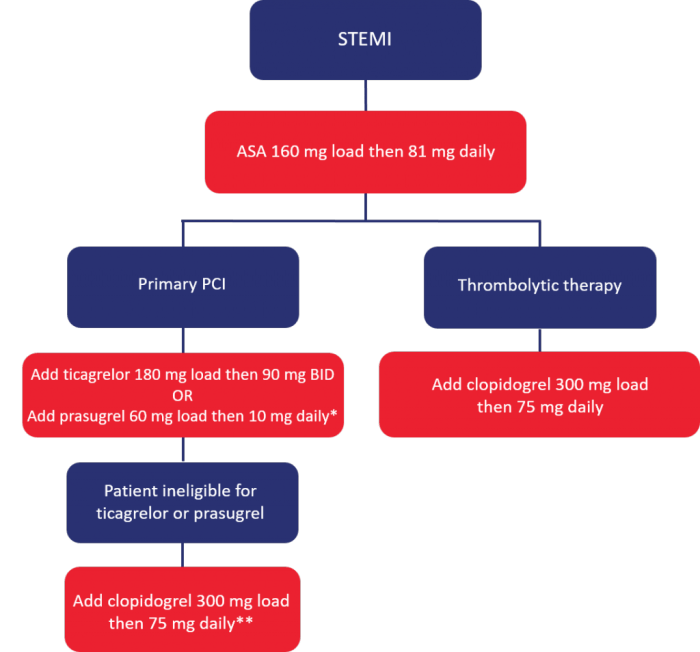
Pharmacological management of STEMI patients involves administering medications to prevent further clot formation, reduce myocardial oxygen demand, and improve cardiac function.
- Antiplatelet therapy:
- Aspirin
- Clopidogrel
- Prasugrel
- Anticoagulants:
- Heparin
- Enoxaparin
- Warfarin
- Beta-blockers:
- Metoprolol
- Carvedilol
- Bisoprolol
- Nitrates:
- Nitroglycerin
- Isosorbide dinitrate
- Statins:
- Atorvastatin
- Rosuvastatin
- Simvastatin
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are essential for STEMI patients to prevent recurrent cardiovascular events and improve overall health.
- Smoking cessation: Smoking is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and should be discontinued immediately.
- Healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
- Regular exercise: Regular physical activity can improve heart health and reduce the risk of obesity.
- Stress management: Stress can contribute to cardiovascular disease. Techniques such as meditation and yoga can help manage stress levels.
Rehabilitation and Secondary Prevention
Cardiac rehabilitation is an important component of recovery for STEMI patients. It involves a supervised program of exercise, education, and counseling to improve physical and psychological well-being.
- Components of cardiac rehabilitation:
- Exercise training
- Education about heart disease and risk factor management
- Counseling for stress management and lifestyle changes
- Benefits of cardiac rehabilitation:
- Improved exercise capacity
- Reduced risk of recurrent cardiovascular events
- Improved quality of life
Question Bank
What are the key components of STEMI management?
The key components of STEMI management include early recognition, rapid reperfusion therapy, optimal medical therapy, and comprehensive rehabilitation.
What is the role of lifestyle modifications in STEMI management?
Lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation, regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, and stress management, play a vital role in reducing the risk of recurrent cardiovascular events and improving overall health outcomes in STEMI patients.
What are the benefits of cardiac rehabilitation for STEMI patients?
Cardiac rehabilitation programs offer numerous benefits for STEMI patients, including improved exercise capacity, reduced symptoms, enhanced quality of life, and decreased risk of future cardiac events.