Conduit that passes from a classified location – Conduits that pass through classified locations demand meticulous attention to security and installation procedures. This comprehensive guide delves into the types of conduits, security considerations, installation protocols, and maintenance requirements to ensure the integrity and safety of these critical systems.
Understanding the unique challenges and best practices associated with conduits in classified locations empowers professionals to mitigate risks, maintain compliance, and safeguard sensitive information.
Types of Conduits
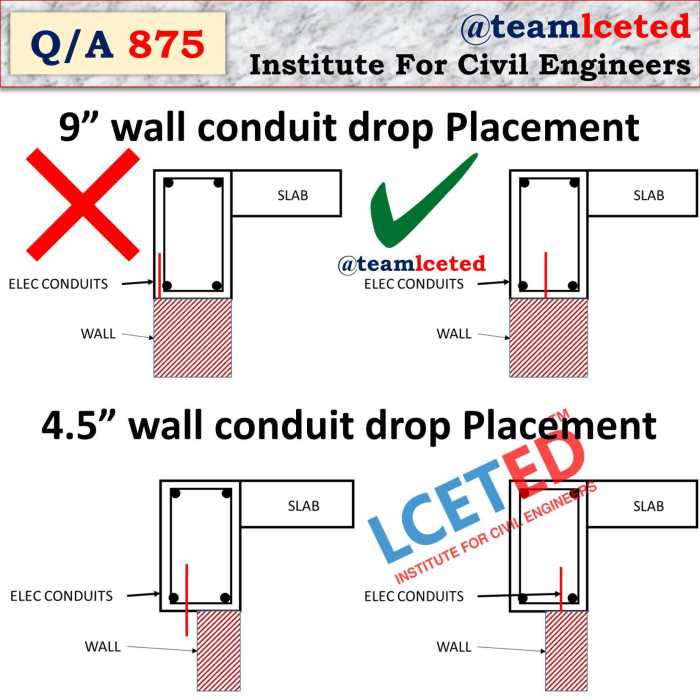
Conduits that can pass through a classified location include:
- Rigid metal conduits (RMC): Made of galvanized steel or aluminum, providing excellent protection against physical damage and corrosion.
- Intermediate metal conduits (IMC): Similar to RMC but with a thinner wall, offering flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
- Electrical metallic tubing (EMT): Lightweight and flexible, suitable for concealed installations where physical protection is not a major concern.
- Flexible metal conduits (FMC): Highly flexible, ideal for use in tight spaces or where vibration is present.
- Non-metallic conduits: Made of materials such as PVC or fiberglass, offering corrosion resistance and ease of installation.
Security Considerations
Passing a conduit through a classified location requires strict security measures to prevent unauthorized access:
- Conduit seals: Installed at the point of entry and exit, creating a physical barrier against intrusion.
- Penetrations: Conduits must pass through fire-rated walls or floors, maintaining the integrity of the fire barrier.
- Access control: Restricted access to areas where conduits pass through classified locations, ensuring only authorized personnel can handle them.
- Surveillance: Cameras or motion detectors monitor conduit entry and exit points, deterring unauthorized access.
Failure to follow security procedures can result in breaches of classified information or physical harm to personnel.
Installation Procedures: Conduit That Passes From A Classified Location

Installing a conduit through a classified location requires meticulous attention to detail:
- Plan and coordinate: Determine the route, type of conduit, and security measures.
- Prepare the penetration: Create openings in walls or floors, ensuring fire-rated integrity.
- Install conduit seals: Place seals at the entry and exit points, following manufacturer’s instructions.
- Route the conduit: Securely fasten the conduit along the designated path, using appropriate fittings and supports.
- Terminate the conduit: Connect the conduit to electrical equipment, ensuring proper grounding and bonding.
Diagrams or illustrations can enhance understanding of the installation process.
Maintenance and Inspection
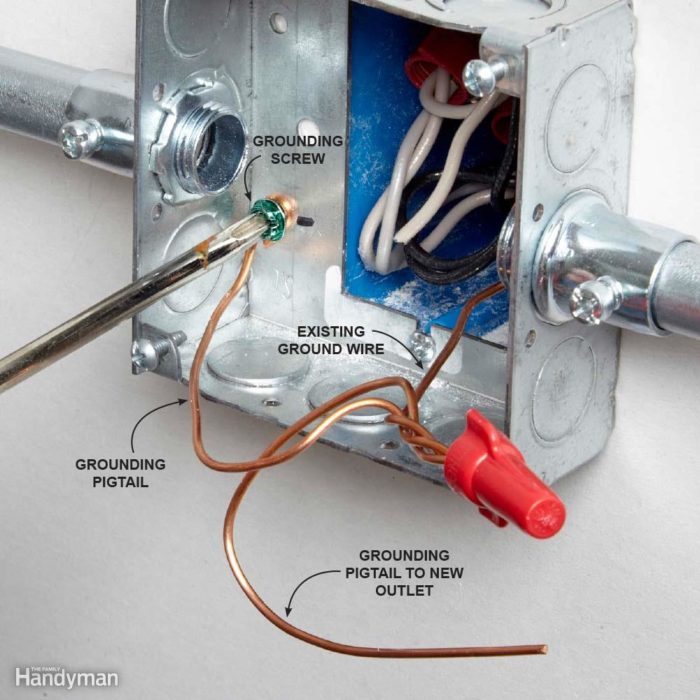
Regular maintenance and inspection are crucial for ensuring the integrity of conduits in classified locations:
- Visual inspections: Regularly check conduits for physical damage, corrosion, or leaks.
- Electrical testing: Test conduits for continuity, grounding, and insulation resistance.
- Seal inspection: Examine conduit seals for damage or deterioration, ensuring they remain effective.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of inspections and maintenance activities.
Neglecting maintenance and inspection can lead to security breaches, electrical hazards, or damage to classified equipment.
General Inquiries
What types of conduits are suitable for classified locations?
Rigid metal conduits, flexible metal conduits, and non-metallic conduits are commonly used in classified locations, each with specific advantages and disadvantages.
What are the key security considerations for conduits in classified locations?
Ensuring physical security, preventing unauthorized access, maintaining electrical integrity, and implementing proper grounding and bonding are crucial security considerations.
What are the consequences of failing to follow security procedures for conduits in classified locations?
Negligence in adhering to security protocols can lead to data breaches, equipment damage, safety hazards, and legal liabilities.