The endocrine system hormone case study analysis delves into the intricate interplay between hormones and the human body, providing a comprehensive understanding of their physiological functions, regulation, and implications in health and disease.
This analysis examines the structure and function of the endocrine system, exploring the role of hormones in regulating various bodily processes. It highlights the major endocrine glands, their respective hormones, and their functions, providing a foundational understanding of the endocrine system’s role in maintaining homeostasis.
Endocrine System Overview
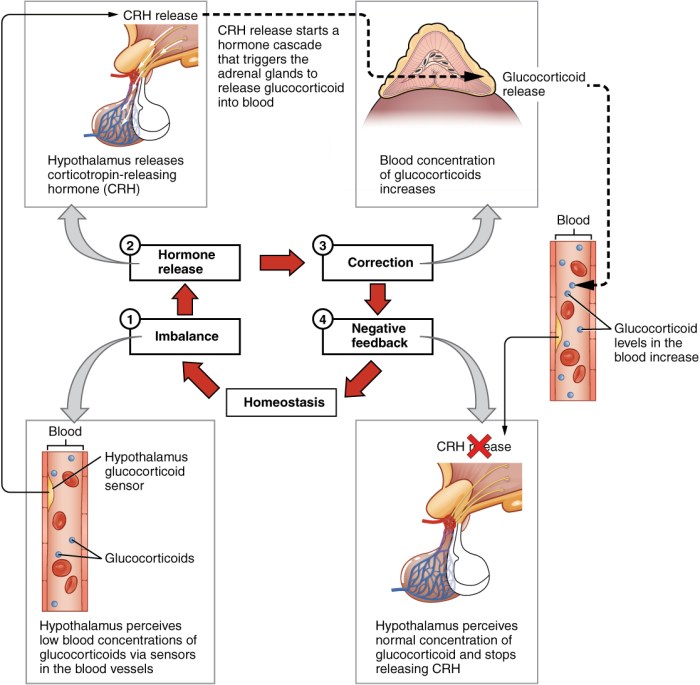
The endocrine system is a network of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily processes, including metabolism, growth, reproduction, and mood.
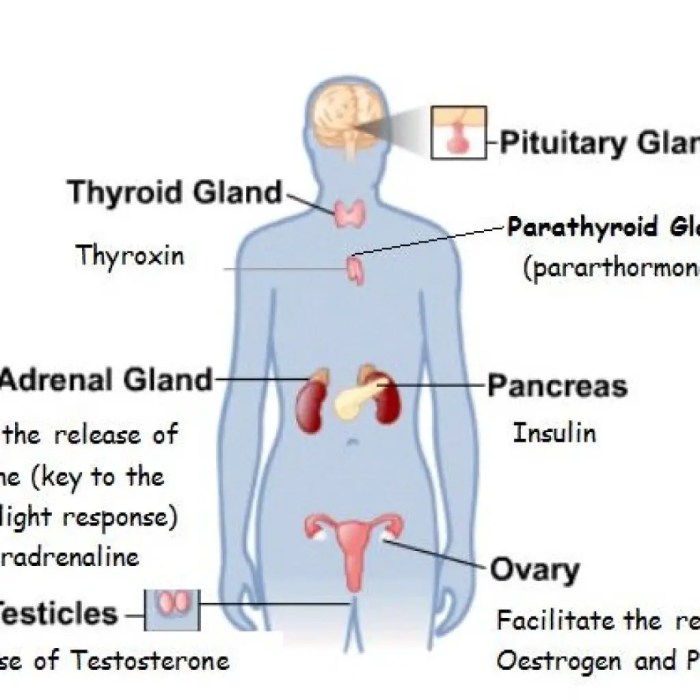
The endocrine system consists of the following major glands:
- Pituitary gland
- Thyroid gland
- Parathyroid glands
- Adrenal glands
- Pancreas
- Ovaries (in females)
- Testes (in males)
Each gland produces specific hormones that target specific organs or tissues. For example, the pituitary gland secretes growth hormone, which promotes growth and development, while the thyroid gland secretes thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism.
Hormone Case Study
Insulin, Endocrine system hormone case study analysis
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas. It regulates blood sugar levels by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy production.
Dysregulation of insulin can lead to diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder in which the body becomes resistant to insulin, leading to impaired glucose uptake by cells.
Symptoms of diabetes include excessive thirst, frequent urination, weight loss, and fatigue. Diagnosis is confirmed through blood tests that measure blood sugar levels.
Endocrine System and Disease
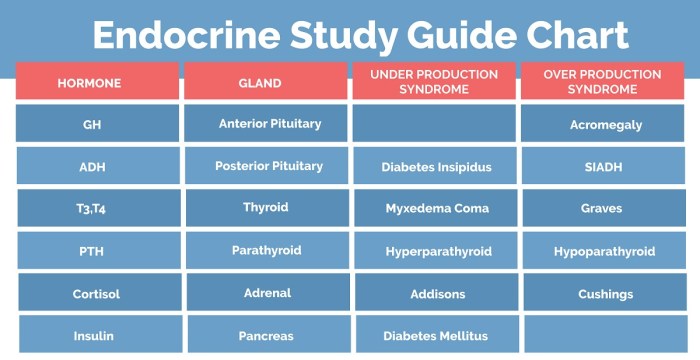
Common endocrine disorders include:
- Diabetes
- Thyroid disorders (e.g., hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism)
- Cushing’s syndrome (excess cortisol production)
- Addison’s disease (deficient cortisol production)
- Growth hormone disorders
Diagnostic procedures for endocrine disorders include blood tests, imaging tests (e.g., ultrasound, MRI), and genetic testing.
Treatment options for endocrine disorders vary depending on the specific condition. They may include medications, surgery, or lifestyle modifications (e.g., diet, exercise).
Essential Questionnaire: Endocrine System Hormone Case Study Analysis
What is the primary function of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system’s primary function is to regulate various physiological processes through the secretion of hormones, which act as chemical messengers.
How are hormones regulated?
Hormone regulation involves feedback mechanisms, where hormone levels are monitored and adjusted to maintain homeostasis.
What are the common symptoms of endocrine disorders?
Symptoms of endocrine disorders vary depending on the specific hormone affected but may include fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and reproductive irregularities.