Embark on an extraordinary journey through time as we delve into Fiveable AP World Unit 1, where the origins of civilization and the rise of humankind unfold before our very eyes. From the fertile banks of the Nile to the bustling streets of ancient Rome, we will unravel the secrets of the past and discover the foundations of our present.
Our exploration will span vast epochs, tracing the evolution of human societies from their humble beginnings to the transformative era of the Renaissance. Along the way, we will encounter towering civilizations, groundbreaking ideas, and pivotal events that have shaped the course of history.
Unit Overview: Fiveable Ap World Unit 1
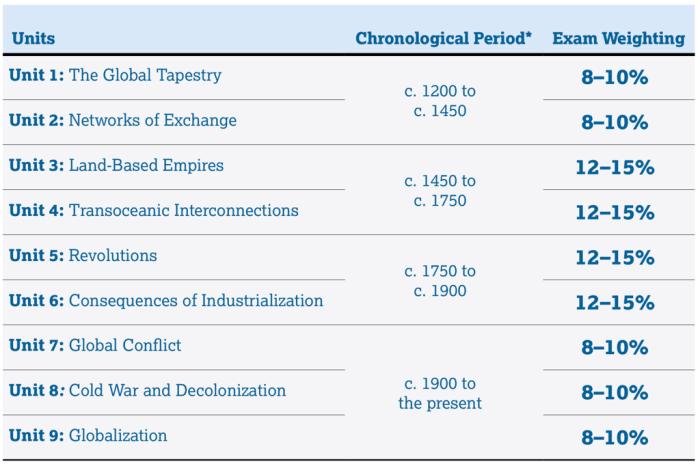
Unit 1 of Fiveable AP World History covers the period from the Paleolithic Era to the rise of civilizations in the river valleys of Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, and China. The unit aims to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the origins of humankind, the development of early societies, and the emergence of complex civilizations.
Key events covered in the unit include:
- The emergence of Homo sapiens in Africa
- The development of agriculture and the Neolithic Revolution
- The rise of the first civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, India, and China
The Origins of Civilization
The emergence of civilization, a complex and transformative process, has been a subject of fascination and inquiry for centuries. Theories abound regarding its origins, each offering unique insights into the factors that fostered the transition from nomadic existence to settled societies.
One prominent theory attributes the rise of civilization to environmental factors. The advent of agriculture, particularly in regions with fertile soil and reliable water sources, provided a stable food supply that allowed populations to grow and settle in one place.
This sedentary lifestyle facilitated the development of specialized skills, trade, and social stratification.
Mesopotamia and Egypt: Cradles of Civilization
Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, and Egypt, along the Nile River, stand as prime examples of early civilizations. Both regions benefited from favorable geographic conditions that supported agriculture and enabled the emergence of complex societies.
- Mesopotamia:Known as the “cradle of civilization,” Mesopotamia was home to the Sumerians, who developed cuneiform writing, advanced mathematics, and sophisticated irrigation systems.
- Egypt:Along the fertile Nile River, Egyptian civilization flourished with its monumental architecture, including the pyramids and the Sphinx, as well as its advancements in astronomy, medicine, and hieroglyphic writing.
The Classical Age
The Classical Age marks a pivotal period in human history, characterized by the emergence of sophisticated civilizations in Greece and Rome. These civilizations laid the foundations for Western culture and left an enduring legacy on global thought, politics, and society.
Comparing Greece and Rome
Both Greece and Rome emerged as powerful city-states that played a significant role in shaping the Mediterranean world. However, they exhibited distinct characteristics that set them apart:
- Political Systems:Greece was a collection of independent city-states, each with its unique form of government. Athens developed a democratic system, while Sparta adopted an oligarchy. Rome, on the other hand, evolved from a monarchy to a republic and eventually an empire.
- Economic Base:Greece’s economy was based on trade and maritime commerce, while Rome’s was founded on agriculture and military conquest. Greece established colonies throughout the Mediterranean, facilitating trade and cultural exchange.
- Cultural Achievements:Greece made remarkable contributions to philosophy, literature, art, and architecture. Rome, while influenced by Greek culture, developed its own distinctive style in literature, engineering, and law.
Political Developments in Greece and Rome
Greece:
- Athenian Democracy:Athens established a democratic system in the 5th century BC, allowing all male citizens to participate in government. This system emphasized citizen involvement, freedom of speech, and the rule of law.
- Spartan Oligarchy:Sparta adopted an oligarchic system, ruled by a small group of wealthy and powerful individuals. The Spartan government focused on military strength and discipline, emphasizing the role of the citizen-soldier.
Rome:
- Roman Republic:Rome transitioned from a monarchy to a republic in the 6th century BC. The republic was governed by a senate and assemblies, allowing for a more representative form of government.
- Roman Empire:In the 1st century BC, Rome established an empire under the rule of Augustus Caesar. The empire expanded across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East, creating a vast and centralized state.
Economic Developments in Greece and Rome
Greece:
- Trade and Commerce:Greece’s economy relied heavily on trade and maritime commerce. Greek merchants established colonies throughout the Mediterranean, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas.
- Athenian Empire:Athens formed the Delian League, an alliance of city-states that provided economic and military support. This empire allowed Athens to control trade routes and amass wealth.
Rome:
- Agriculture and Conquest:Rome’s economy was primarily based on agriculture. Roman farmers cultivated vast estates and produced surplus crops. Military conquest also played a significant role in the Roman economy, as Rome acquired wealth and resources from conquered territories.
- Roman Roads and Infrastructure:The Romans constructed an extensive network of roads and infrastructure, facilitating trade and communication across the empire.
Cultural Developments in Greece and Rome
Greece:
- Philosophy and Science:Greek philosophers, such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle, made significant contributions to the development of Western thought. Greek scientists, such as Pythagoras and Euclid, advanced mathematics and geometry.
- Literature and Drama:Greek literature flourished with epic poems, such as Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey, and dramatic works by Sophocles and Euripides.
- Art and Architecture:Greek artists and architects created iconic sculptures, temples, and theaters that showcased their technical skill and aesthetic sensibilities.
Rome:
- Literature and Law:Roman literature was influenced by Greek models but developed its own distinctive style. Roman historians, such as Livy and Tacitus, recorded the empire’s history. Roman law, codified in the Corpus Juris Civilis, became the foundation of legal systems in many Western countries.
- Engineering and Architecture:The Romans excelled in engineering and architecture. They built aqueducts, bridges, and amphitheaters that demonstrated their technological prowess.
- Religion and Culture:Roman religion was a blend of indigenous beliefs and Greek influences. The Romans also adopted many Greek cultural practices, such as public baths and chariot races.
Impact of Classical Civilization on Western Culture
The Classical Age of Greece and Rome had a profound impact on Western culture. Greek philosophy, literature, art, and science laid the groundwork for Western intellectual thought. Roman law, political systems, and engineering achievements provided the foundation for many modern institutions and technologies.
The legacy of classical civilization continues to shape Western values, ideas, and ways of life.
The Middle Ages
The Middle Ages, also known as the Medieval Period, lasted from the 5th to the 15th centuries. It was a time of significant political and religious change in Europe.
Political Developments
* The Roman Empire collapsed in the 5th century, leading to the rise of smaller, independent kingdoms.
Fiveable AP World Unit 1 is a great resource for students who are studying for the AP World History exam. The unit covers a wide range of topics, including the origins of civilization, the rise and fall of empires, and the development of global interactions.
While the unit is comprehensive, it can also be challenging at times. One of the more difficult concepts that students often struggle with is ca h2po3 2 compound name . However, by using the resources available on Fiveable, students can gain a better understanding of this concept and improve their overall performance in the unit.
- The feudal system emerged, with nobles granting land to knights in exchange for military service.
- The Catholic Church played a significant role in politics, providing stability and legitimizing the authority of rulers.
Religious Developments
* Christianity became the dominant religion in Europe, with the Catholic Church as its central institution.
- The Church enforced religious orthodoxy through the Inquisition and Crusades.
- Monasteries served as centers of learning and culture, preserving knowledge from ancient times.
The Catholic Church in Medieval Society
* The Catholic Church was a major landowner and had a vast network of monasteries and cathedrals.
- It provided education, healthcare, and social welfare services.
- The Church’s teachings influenced all aspects of medieval life, from art and architecture to social customs.
The Crusades
* The Crusades were a series of religious wars fought between Christians and Muslims for control of the Holy Land.
- They were launched by Pope Urban II in 1095 and lasted for over two centuries.
- The Crusades had a significant impact on European society, leading to increased trade, cultural exchange, and the rise of new kingdoms.
The Renaissance and Reformation
The Renaissance and Reformation were two major cultural and religious movements that transformed Europe during the 15th and 16th centuries. The Renaissance was a period of renewed interest in classical learning and culture, while the Reformation was a religious movement that led to the establishment of Protestantism.
The Renaissance
The Renaissance began in Italy in the 14th century and spread to the rest of Europe by the 16th century. It was a time of great intellectual and artistic achievement. Renaissance thinkers rediscovered the works of ancient Greek and Roman philosophers and artists, and they began to apply these ideas to their own work.
This led to a flowering of art, literature, and science.
- Art:Renaissance artists developed new techniques for painting and sculpture, and they created some of the most famous works of art in history. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael used their skills to capture the beauty of the human form and to depict scenes from classical mythology and history.
- Literature:Renaissance writers also produced some of the greatest works of literature in history. Writers like William Shakespeare, Miguel de Cervantes, and Geoffrey Chaucer used their writing to explore the human condition and to tell stories that would entertain and enlighten their readers.
- Science:Renaissance scientists made important discoveries in astronomy, mathematics, and physics. Nicolaus Copernicus proposed that the sun, not the Earth, was the center of the solar system, and Galileo Galilei developed a telescope that allowed him to observe the moons of Jupiter.
The Reformation, Fiveable ap world unit 1
The Reformation began in Germany in the early 16th century when Martin Luther, a Catholic priest, challenged the authority of the Pope. Luther argued that salvation could only be achieved through faith in Jesus Christ, and he rejected the Catholic Church’s teachings on indulgences, purgatory, and the importance of good works.
Luther’s ideas quickly spread throughout Europe, and by the mid-16th century, Protestantism had become a major force in European Christianity.The Reformation had a profound impact on European society. It led to religious wars, political upheaval, and the rise of new nations.
It also had a major impact on the development of Western culture, as Protestantism emphasized the importance of education and individual conscience.
- Causes:The Reformation was caused by a number of factors, including the rise of humanism, the decline of the Catholic Church, and the invention of the printing press.
- Consequences:The Reformation had a number of consequences, including the rise of Protestantism, the decline of the Catholic Church, and the outbreak of religious wars.
FAQ
What is the scope of Fiveable AP World Unit 1?
Fiveable AP World Unit 1 covers the period from the origins of civilization to the Protestant Reformation, spanning approximately 5,000 years of human history.
What are the key events covered in Fiveable AP World Unit 1?
Some of the key events covered include the rise of Mesopotamia and Egypt, the development of classical Greece and Rome, the spread of Christianity, the Islamic conquests, and the Renaissance.
How does Fiveable AP World Unit 1 prepare students for the AP exam?
Fiveable AP World Unit 1 provides students with a comprehensive overview of the content covered on the AP World History exam. The unit includes engaging videos, practice questions, and expert guidance to help students succeed on the exam.


